2026 Data Interoperability Mandates: A 7-Step Compliance Checklist for Healthcare Providers

Preparing for the 2026 data interoperability mandates is essential for healthcare providers to facilitate seamless information exchange, enhance patient care, and ensure regulatory adherence across the United States.
Are you a healthcare provider in the U.S. ready for the seismic shift coming in 2026? The landscape of patient data management is evolving rapidly, and preparing for the 2026 data interoperability mandates is no longer optional. These impending regulations promise to revolutionize how patient information is accessed, shared, and utilized, fundamentally reshaping clinical workflows and administrative processes. Understanding and implementing a robust compliance strategy now is paramount for maintaining operational efficiency, enhancing patient outcomes, and avoiding significant penalties. Let’s delve into a practical 7-step checklist designed to guide your organization toward full compliance.
Understanding the 2026 Data Interoperability Mandates
The 2026 data interoperability mandates represent a critical juncture for the U.S. healthcare system, aiming to break down information silos and foster a truly connected care ecosystem. These mandates, stemming from federal initiatives like the 21st Century Cures Act, are designed to empower patients with greater access to their health information and enable seamless data exchange among providers, payers, and public health agencies. Ultimately, the goal is to improve care coordination, reduce medical errors, and drive innovation in value-based care models.
For healthcare providers, this means a significant shift from traditional, often fragmented, data management practices to a more integrated and standardized approach. Non-compliance could lead to severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and a hinderance to participating in advanced care programs. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of these mandates is the first step toward successful preparation and implementation.
Key Regulatory Drivers
Several legislative and regulatory frameworks underpin the 2026 mandates. These include:
- The 21st Century Cures Act: This landmark legislation from 2016 aims to accelerate medical product development and bring innovations to patients faster, while also driving interoperability and preventing information blocking.
- ONC’s Cures Act Final Rule: Issued by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), this rule implements key provisions of the Cures Act, focusing on information blocking, application programming interfaces (APIs), and certified health IT.
- CMS Interoperability and Patient Access Rule: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) rule focuses on improving patient access to their health information and promoting interoperability between payers and providers.
These regulations collectively establish the foundation for the upcoming 2026 requirements, emphasizing standardized data formats, secure data exchange, and patient-centric access. Providers must familiarize themselves with the specifics of each to ensure their strategies align with federal expectations.
The essence of these mandates is to move towards a future where patient health information flows freely and securely, supporting informed decision-making and collaborative care. This shift requires not just technological upgrades but also a cultural transformation within healthcare organizations to embrace data sharing as a core principle of patient care.
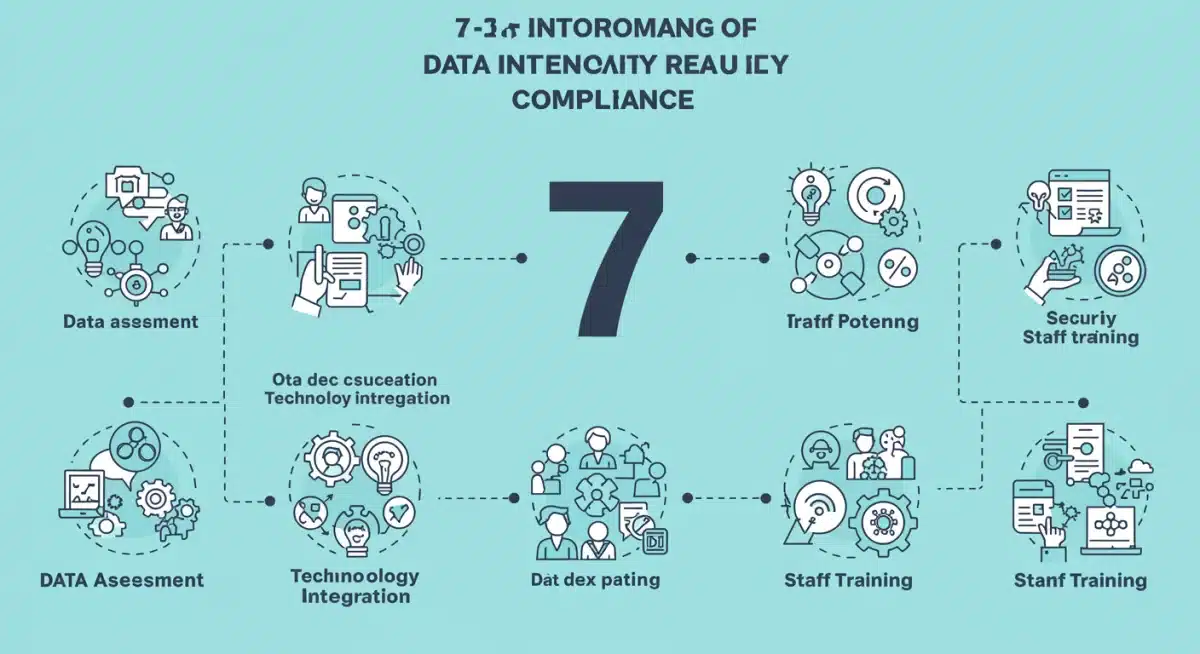
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive Data Audit and Gap Analysis
The initial and perhaps most critical step in preparing for the 2026 data interoperability mandates is to thoroughly understand your current data landscape. A comprehensive data audit involves cataloging all existing patient data, identifying its sources, formats, and storage locations. This detailed inventory provides the foundation for identifying where your organization stands in relation to the upcoming compliance requirements.
Following the audit, a gap analysis will pinpoint discrepancies between your current data practices and the mandated interoperability standards. This includes assessing your electronic health record (EHR) system’s capabilities, identifying any legacy systems that hold critical patient information, and evaluating your current data exchange protocols. Understanding these gaps early allows for strategic planning and resource allocation.
Identifying Data Silos and Inefficiencies
Many healthcare organizations operate with various disparate systems, leading to data silos that hinder seamless information flow. This step focuses on uncovering these isolated data repositories and understanding why they exist. It’s not uncommon to find patient data stored in departmental-specific systems, paper records, or even outdated software that doesn’t communicate with your primary EHR.
- Map Data Sources: Document every system that collects, stores, or transmits patient data, from EHRs to billing systems and specialized clinic software.
- Assess Data Formats: Determine the formats in which your data is currently stored (e.g., HL7, FHIR, DICOM, proprietary formats). The mandates will likely favor standardized formats.
- Evaluate Data Quality: Interoperability is only as good as the data it exchanges. Identify inconsistencies, incompleteness, or inaccuracies in your data that could impede exchange.
By systematically identifying these areas, providers can gain a clear picture of the scale of the challenge and prioritize which systems and data points require immediate attention. This proactive approach minimizes surprises down the line and ensures that all relevant data is considered in your compliance strategy.
A thorough data audit and gap analysis lay the groundwork for all subsequent steps, providing the necessary insights to develop a targeted and effective compliance plan. Without this foundational understanding, any interoperability efforts risk being incomplete or misdirected.
Step 2: Upgrade and Optimize Your Health IT Infrastructure
With a clear understanding of your data landscape, the next step involves making necessary enhancements to your health IT infrastructure. This often means upgrading existing systems, integrating new technologies, and ensuring that all components can communicate effectively. The 2026 mandates place a strong emphasis on modern, interoperable technologies capable of supporting standardized data exchange protocols.
A significant focus will be on your Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. Many older EHR versions may not fully support the required APIs or data standards. Therefore, an upgrade or even a migration to a more advanced EHR system might be necessary. This step also includes evaluating other clinical and administrative systems that interact with patient data to ensure they are compatible with your interoperability goals.
Embracing FHIR and API Capabilities
The Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are central to the upcoming mandates. FHIR provides a flexible and modern framework for exchanging healthcare information, while APIs enable different software applications to communicate with each other seamlessly. Providers must ensure their systems can leverage these technologies.
- EHR System Upgrades: Prioritize upgrading to an EHR version that is certified for information blocking and supports FHIR-based APIs.
- API Integration Strategy: Develop a clear strategy for integrating APIs across your various health IT systems to enable real-time data exchange.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Consider migrating to cloud-based platforms for enhanced scalability, security, and interoperability capabilities.
Investing in modern health IT infrastructure is not just about compliance; it’s about future-proofing your organization. These upgrades can lead to improved operational efficiency, better clinical decision-making, and a more streamlined patient experience. The right infrastructure will serve as the backbone for your interoperability efforts, allowing for secure and efficient data flow.
Optimizing your health IT infrastructure is a substantial undertaking that requires careful planning, budget allocation, and potentially external expertise. However, it’s an investment that will pay dividends in terms of compliance, efficiency, and ultimately, patient care quality.
Step 3: Implement Robust Data Governance and Security Protocols
Interoperability without robust data governance and security is a recipe for disaster. As data flows more freely, the risks of breaches and misuse increase. This step focuses on establishing comprehensive policies and technologies to protect patient information while facilitating its exchange. The 2026 mandates reinforce existing privacy regulations like HIPAA and introduce new expectations for data security.
Data governance defines who is responsible for data, how it’s managed, and the rules for its use. Security protocols involve the technical safeguards and processes put in place to prevent unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of information. Both are critical for building trust and ensuring the ethical handling of sensitive patient data.
Strengthening Privacy and Compliance Frameworks
Beyond technical measures, organizations must develop and enforce clear policies and procedures for data handling. This includes consent management, data retention, and breach response plans. Regular audits and risk assessments are also vital to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
- Data Access Controls: Implement strict role-based access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can view or modify patient data.
- Encryption and Anonymization: Utilize encryption for data at rest and in transit, and consider anonymization techniques where appropriate for research or public health initiatives.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits and penetration testing to identify and remediate potential vulnerabilities in your systems.
A strong data governance framework ensures that all staff understand their responsibilities regarding data privacy and security. It also provides a clear roadmap for how data should be managed throughout its lifecycle, from collection to archival. This holistic approach to security and governance is non-negotiable in an increasingly interconnected healthcare environment.
Implementing robust data governance and security protocols is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. It requires continuous vigilance, adaptation to evolving threats, and a commitment from leadership to prioritize patient data protection above all else.
Step 4: Establish Standardized Data Exchange Agreements
Achieving true interoperability extends beyond internal systems; it requires effective collaboration with external partners, including other healthcare providers, payers, and health information exchanges (HIEs). This step involves establishing clear and legally sound data exchange agreements that outline the terms, conditions, and technical specifications for sharing patient information.
These agreements are crucial for defining data ownership, responsibilities regarding data security, and the protocols for data transmission. Without standardized agreements, the free flow of information can be hampered by legal ambiguities and technical incompatibilities. The 2026 mandates implicitly encourage such agreements to facilitate a broader network of interconnected healthcare entities.
Collaborating with External Stakeholders
Successful data exchange relies on trust and mutual understanding among all parties involved. This means actively engaging with your partners to develop agreements that meet everyone’s needs while adhering to regulatory requirements. Consider participating in regional or national HIEs to streamline these processes and leverage established networks.
- Interoperability Agreements: Draft and formalize agreements with frequent data exchange partners, specifying data types, transmission methods, and security requirements.
- Participation in HIEs: Actively engage with Health Information Exchanges (HIEs) to facilitate broader and more secure data sharing across the healthcare ecosystem.
- Vendor Partnerships: Work closely with your EHR and other IT vendors to ensure their solutions support your data exchange needs and comply with future mandates.
Standardized data exchange agreements reduce administrative burden, clarify responsibilities, and ensure that data sharing is conducted in a consistent and compliant manner. They are a cornerstone of building a reliable and secure interoperable network, enabling better care coordination and improved patient outcomes.
Establishing these agreements requires legal expertise, technical coordination, and a spirit of collaboration. Proactive engagement with partners now will ensure that your organization is well-positioned for seamless data exchange when the 2026 mandates fully take effect.
Step 5: Develop a Comprehensive Staff Training Program
Technology and policies are only as effective as the people who use them. A critical component of preparing for the 2026 data interoperability mandates is ensuring that all staff members, from clinicians to administrative personnel, are adequately trained on new systems, protocols, and their responsibilities regarding data exchange and privacy. A well-informed workforce is your strongest defense against compliance failures and data breaches.
Training should not be a one-time event but an ongoing process that adapts to new updates and evolving threats. It must cover not only the technical aspects of using interoperable systems but also the ethical and legal implications of sharing patient data. Emphasize the importance of patient consent, data security, and the role each individual plays in maintaining compliance.
Empowering Your Workforce for Interoperability
Tailor training programs to different roles within your organization, focusing on the specific tasks and data interactions relevant to each group. Clinical staff, for example, will need training on accessing and interpreting external patient data, while administrative staff may focus on consent management and data request processing.
- Role-Specific Training Modules: Create customized training modules that address the unique needs and responsibilities of different departments and roles.
- Regular Refresher Courses: Implement mandatory annual or semi-annual refresher courses to keep staff updated on best practices and any regulatory changes.
- Simulated Scenarios: Use simulated data exchange scenarios to help staff practice new workflows and respond effectively to potential issues.
An empowered and knowledgeable workforce is essential for the successful adoption of interoperable systems. When staff understand the ‘why’ behind the mandates and feel confident in using new tools, they become advocates for the changes, leading to smoother transitions and greater compliance. This human element is often underestimated but is vital for long-term success.
Investing in comprehensive staff training demonstrates a commitment to compliance and fosters a culture of responsibility and excellence in data management. It ensures that your organization is not only technologically ready but also human-ready for the demands of 2026.
Step 6: Implement Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Achieving compliance with the 2026 data interoperability mandates is not a static goal; it’s an ongoing journey. This step emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and evaluation of your interoperability efforts to ensure sustained compliance, identify emerging issues, and adapt to future changes. The healthcare landscape is dynamic, and your compliance strategy must be equally agile.
Continuous monitoring involves regularly reviewing data exchange processes, system performance, and security logs. Evaluation takes this a step further by analyzing the effectiveness of your compliance measures, identifying areas for improvement, and assessing the impact of interoperability on patient care and operational efficiency. This iterative process allows for constant refinement and optimization.
Adaptive Compliance Strategies
The regulatory environment can evolve, and new technologies will emerge. Your monitoring and evaluation framework should be flexible enough to incorporate these changes without significant disruption. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) related to interoperability, such as data exchange success rates, security incident frequency, and user adoption rates.
- Performance Dashboards: Develop dashboards to track key interoperability metrics, providing real-time insights into system performance and data exchange efficiency.
- Regular Compliance Audits: Conduct internal and external audits to verify adherence to regulatory requirements and identify any non-compliance issues.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish channels for staff and patients to provide feedback on interoperability processes, helping to identify practical challenges and solutions.
By continuously monitoring and evaluating your interoperability posture, your organization can proactively address challenges, mitigate risks, and ensure that your systems and processes remain compliant and effective. This proactive approach not only helps avoid penalties but also drives continuous improvement in patient care and operational excellence.
An effective monitoring and evaluation framework transforms compliance from a burdensome obligation into an opportunity for ongoing improvement and innovation. It ensures that your organization remains at the forefront of healthcare data management, ready to meet the demands of an evolving digital health ecosystem.
Step 7: Engage with MedTech Innovators and Policy Updates
The final step in preparing for the 2026 data interoperability mandates involves maintaining an active awareness of the broader MedTech landscape and staying informed about ongoing policy developments. The field of healthcare technology is constantly innovating, with new solutions emerging that can further enhance interoperability, security, and patient engagement. Similarly, healthcare policy is not static; regulations can be refined or expanded.
Engaging with MedTech innovators means exploring new tools and platforms that can complement your existing infrastructure or address specific interoperability challenges. This could include advanced analytics platforms, AI-powered data integration tools, or cutting-edge telehealth solutions that leverage interoperable data. Staying abreast of policy updates ensures your compliance strategy remains aligned with the latest legal and ethical guidelines.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies and Policy Insights
Active participation in industry forums, conferences, and partnerships with MedTech startups can provide valuable insights and opportunities. These engagements can help you discover innovative solutions that not only ensure compliance but also drive competitive advantage and improve patient outcomes. Similarly, subscribing to official government publications and industry analyses will keep you informed about any regulatory shifts.
- Pilot New Technologies: Consider piloting innovative MedTech solutions that promise to enhance interoperability, such as AI-driven data cleansing or secure data sharing platforms.
- Participate in Industry Groups: Join healthcare technology associations and interoperability working groups to share best practices and influence future policy.
- Monitor Regulatory Bodies: Regularly review publications from ONC, CMS, and other relevant regulatory bodies for updates and guidance on interoperability mandates.
By actively engaging with MedTech innovators and staying informed about policy updates, healthcare providers can ensure their interoperability strategy is not only compliant but also forward-thinking. This proactive engagement will allow your organization to leverage the full potential of interconnected health data, driving innovation in patient care and operational efficiency.
This ongoing engagement ensures that your organization is not just reacting to mandates but actively shaping its future in a digitally connected healthcare world. It positions you as a leader in adopting advanced technologies and policies that benefit both your organization and the patients you serve.
| Key Compliance Step | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Data Audit & Gap Analysis | Identify current data landscape, formats, storage, and discrepancies with 2026 mandates. |
| IT Infrastructure Upgrade | Enhance EHR systems and integrate APIs for FHIR-based data exchange. |
| Data Governance & Security | Implement robust policies and technical safeguards to protect patient data during exchange. |
| Staff Training & Education | Educate all personnel on new systems, data sharing protocols, and privacy responsibilities. |
Frequently Asked Questions About 2026 Interoperability
The primary goals are to enhance patient access to their health information, improve care coordination among providers, reduce information blocking, and facilitate seamless, secure data exchange across the U.S. healthcare ecosystem to drive better patient outcomes and innovation.
Small practices will need to invest in compliant EHR systems and staff training. While challenging, resources and incentives are often available. Compliance ensures they can participate in modern care networks and avoid penalties, ultimately improving patient care and operational efficiency.
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) is the preferred standard for exchanging healthcare data, and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) enable different systems to communicate using this standard. They are crucial for real-time, secure, and standardized data exchange, forming the technical backbone of interoperability.
Non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties, exclusion from certain federal programs, reputational damage, and a hinderance to providing coordinated patient care. It can also limit access to shared patient data, impacting clinical decision-making and operational efficiency.
Providers should regularly monitor official publications from the ONC, CMS, and other relevant regulatory bodies. Engaging with industry associations and professional networks also provides timely insights and best practices for navigating the evolving landscape of healthcare policy and technology.
Conclusion
Preparing for the 2026 data interoperability mandates is a multifaceted but essential endeavor for all U.S. healthcare providers. By systematically addressing each step of this compliance checklist—from conducting thorough data audits and upgrading IT infrastructure to implementing robust security, fostering external collaboration, training staff, and continuous monitoring—organizations can confidently navigate the evolving regulatory landscape. Embracing these changes not only ensures compliance but also unlocks significant opportunities for enhanced patient care, operational efficiency, and innovation within the dynamic MedTech environment. Proactive engagement with these mandates will position healthcare providers at the forefront of a more connected and patient-centric future.