Telehealth Platform EHR Integration: 2026 Comparison

Telehealth EHR integration 2026 is pivotal for healthcare, with platforms now offering over 95% compatibility with EHR systems, streamlining clinical workflows and significantly enhancing patient care delivery.
As we navigate the evolving landscape of healthcare technology in 2026, the seamless integration of telehealth solutions with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems has become not just a desideratum but a critical necessity. This article delves into a comprehensive comparison of leading telehealth EHR integration 2026 capabilities, aiming to inform healthcare providers about achieving optimal interoperability and patient care.
The Imperative of Seamless EHR Integration in Telehealth
The acceleration of telehealth adoption has profoundly reshaped healthcare delivery, making the underlying technological infrastructure more critical than ever. In 2026, the effectiveness of any telehealth platform is intrinsically linked to its ability to seamlessly integrate with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. This integration is not merely about data exchange; it’s about creating a unified, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem where information flows effortlessly, reducing administrative burden and enhancing clinical decision-making.
Without robust EHR integration, telehealth can become a siloed service, leading to fragmented patient data, potential medical errors, and clinician burnout due as they toggle between disparate systems. The goal for 2026 is to achieve at least 95% compatibility, ensuring that patient histories, diagnostic results, treatment plans, and billing information are instantly accessible and updated across all care modalities. This level of integration supports continuity of care, improves patient safety, and ultimately drives better health outcomes.
Challenges in Achieving High-Level Integration
While the benefits are clear, achieving truly seamless integration presents various challenges. These often stem from legacy EHR systems, differing data standards, and security concerns. However, advancements in API development, cloud computing, and standardized interoperability frameworks are rapidly mitigating these hurdles.
- Legacy System Complexity: Older EHR systems may lack modern API capabilities, complicating real-time data exchange.
- Data Standardization: Variations in how different systems store and categorize patient data require sophisticated mapping.
- Security and Compliance: Ensuring HIPAA compliance and data privacy during integration adds layers of complexity.
- Cost and Resources: Initial integration efforts can be resource-intensive, requiring significant investment in IT infrastructure and personnel.
Overcoming these challenges requires strategic planning, collaboration between telehealth vendors and EHR providers, and a commitment to adopting open standards. The future of telehealth hinges on these integrated solutions, promising a more connected and responsive healthcare experience for both providers and patients.
Key Integration Capabilities to Look for in 2026 Telehealth Platforms
When evaluating telehealth platforms in 2026, specific integration capabilities stand out as essential for achieving high compatibility with EHR systems. These features go beyond basic data transfer, focusing on deep, bidirectional synchronization that supports dynamic clinical workflows and administrative efficiency. Understanding these capabilities is crucial for healthcare organizations aiming to future-proof their digital health infrastructure.
The ideal telehealth platform should act as an extension of the EHR, not just a separate application. This means real-time data updates, automated scheduling, and integrated billing are paramount. Providers need to access a complete patient record during a virtual visit, just as they would in a face-to-face consultation, ensuring consistent and informed care.
Advanced API and Interoperability Standards
Modern telehealth platforms leverage advanced Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and adhere to industry-standard interoperability protocols. These include FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7, which are critical for enabling efficient, secure, and standardized data exchange between disparate systems.
- FHIR APIs: Facilitate granular data access and updates, supporting a wide range of clinical and administrative workflows.
- HL7 Integration: Essential for messaging and data exchange, particularly for traditional healthcare data formats.
- Bidirectional Data Flow: Ensures that data entered in the telehealth platform instantly updates the EHR, and vice versa, preventing data discrepancies.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Streamlines user access by allowing clinicians to log in once and access both systems without re-authenticating.
Beyond technical standards, the ease of configuring these integrations also plays a significant role. Platforms offering intuitive setup tools and comprehensive documentation can drastically reduce the implementation time and ongoing maintenance burden for IT departments. This focus on user-friendliness extends to the integration process itself, making it accessible even for organizations with limited specialized IT staff.
Leading Telehealth Platforms and Their EHR Integration Strengths
The telehealth market in 2026 is vibrant, with several platforms distinguishing themselves through their robust EHR integration capabilities. These leaders understand that deep interoperability is a competitive advantage, offering solutions that cater to a wide range of healthcare settings, from large hospital systems to small private practices. Their focus on seamless data flow significantly enhances operational efficiency and patient safety.
Examining specific platforms reveals a diverse approach to integration, yet a common thread is the commitment to open standards and flexible API architectures. This allows healthcare providers to choose solutions that best fit their existing EHR infrastructure, minimizing disruption and maximizing return on investment.
Platform A: Deep Clinical Workflow Integration
Platform A is widely recognized for its profound integration with major EHR systems like Epic and Cerner. It offers pre-built connectors that enable real-time synchronization of patient demographics, appointment schedules, clinical notes, and medication lists. This level of integration virtually eliminates manual data entry for virtual visits, allowing clinicians to focus entirely on patient care.
- Pre-built Connectors: Expedite integration with popular EHR systems, reducing setup time.
- Real-time Data Sync: Ensures all patient data is current across both telehealth and EHR platforms.
- Integrated Scheduling: Allows appointments booked via telehealth to automatically appear in the EHR calendar.
- Clinical Note Auto-Population: Telehealth visit notes can be directly pushed into the patient’s EHR chart.
The strength of Platform A lies in its ability to embed telehealth directly into the clinical workflow, making it a natural extension of in-person care. This holistic approach significantly improves efficiency and reduces the chances of fragmented patient records, a common pitfall in less integrated systems.
Assessing Compatibility: What 95% Means for Your Practice
When discussions around telehealth platforms and EHR integration mention ‘95% compatibility,’ it signifies a high degree of interoperability where nearly all critical data points flow seamlessly between systems. This benchmark is crucial for healthcare organizations in 2026, as it directly impacts clinical efficiency, data accuracy, and the overall patient experience. Achieving this level of compatibility means minimizing manual data entry, reducing administrative overhead, and ensuring that clinicians have comprehensive patient information at their fingertips during virtual encounters.
For a healthcare practice, 95% compatibility translates into significant operational advantages. It means less time spent on administrative tasks and more time dedicated to patient care. It also mitigates the risk of medical errors that can arise from incomplete or outdated patient records, fostering a safer and more reliable care environment.
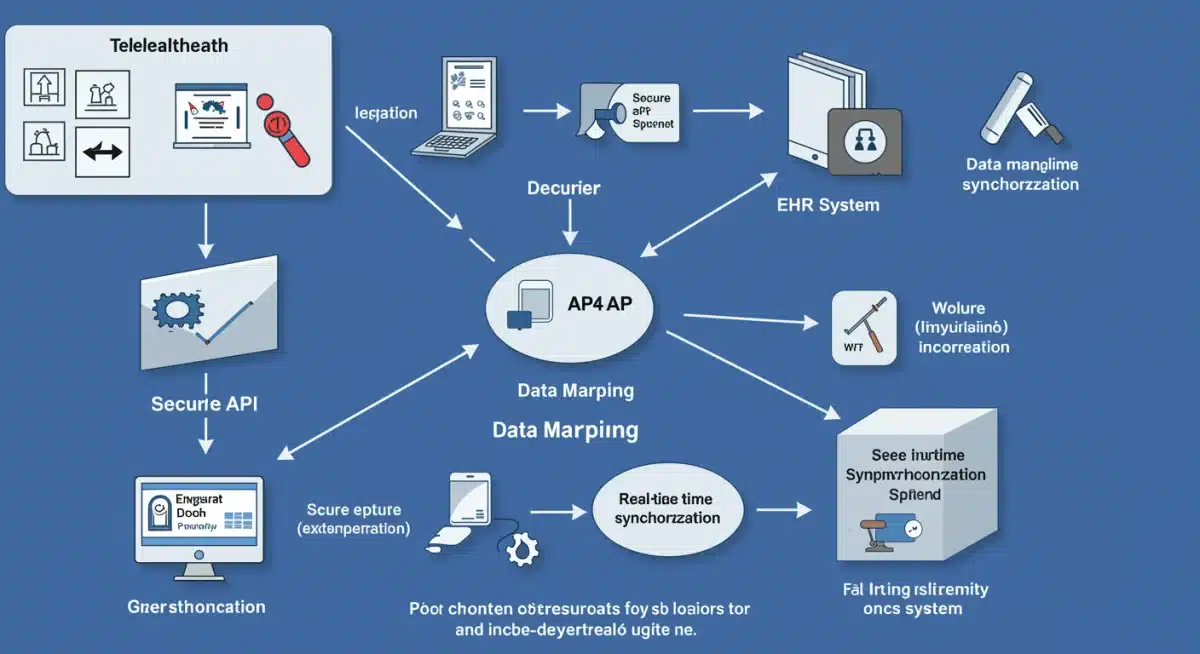
Defining the 95% Compatibility Metric
The 95% compatibility metric typically encompasses several key areas of data exchange and workflow integration:
- Patient Demographics: Automatic synchronization of patient identifiers, contact information, and insurance details.
- Appointment Management: Telehealth scheduling directly updates the EHR calendar, and vice versa.
- Clinical Documentation: Visit summaries, diagnoses, and treatment plans from telehealth sessions are automatically recorded in the EHR.
- Medication Management: Prescriptions and medication history are consistent across both platforms.
- Billing and Coding: Telehealth services are accurately coded and billed through the integrated system.
The remaining 5% often accounts for highly specialized data fields or unique workflow nuances that may require custom configurations or occasional manual intervention. However, the vast majority of routine operations are automated, providing a nearly frictionless experience. Organizations should strive for this benchmark to fully realize the benefits of their telehealth investments.
The Future Landscape: Innovations Driving Further Integration by 2026
The rapid pace of innovation in healthcare technology continues to drive advancements in telehealth and EHR integration. By 2026, several emerging trends and technologies are poised to push compatibility beyond the current 95% benchmark, ushering in an era of truly intelligent and predictive healthcare. These innovations promise to streamline workflows even further, enhance diagnostic capabilities, and personalize patient care on an unprecedented scale.
The focus is shifting towards more proactive and data-driven approaches, where AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics play a pivotal role in optimizing the interaction between telehealth platforms and EHR systems. This evolution will not only improve efficiency but also enable better clinical insights and more effective patient management strategies.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Integration
AI and machine learning are becoming central to enhancing integration capabilities. These technologies can automate complex data mapping, predict potential data discrepancies, and even suggest relevant patient information based on the context of a virtual visit. This proactive intelligence helps prevent errors and ensures a more complete patient picture.
- Automated Data Mapping: AI algorithms learn to accurately map data fields between disparate systems, reducing manual configuration.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning can identify patterns in patient data to flag potential health risks during telehealth consultations.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP tools can extract key information from unstructured clinical notes and integrate it into structured EHR fields.
- Intelligent Workflows: AI can suggest next steps in a patient’s care journey, automating follow-up tasks and referrals.
These AI-driven enhancements move beyond simple data transfer, transforming integration into an intelligent process that actively supports clinical decision-making. The ability of AI to learn and adapt to specific practice needs will be a game-changer for achieving ultimate compatibility and efficiency in healthcare.
Strategic Implementation for Optimal Telehealth-EHR Synergy
Achieving optimal synergy between telehealth platforms and EHR systems in 2026 requires more than just selecting a compatible vendor; it demands a strategic implementation approach. This involves careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and a phased rollout to ensure smooth adoption and maximize the benefits of integrated technology. A well-executed strategy can significantly impact clinical outcomes, operational efficiency, and provider satisfaction.
Organizations must view integration as an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Continuous monitoring, feedback loops, and adaptation to new technologies and regulatory requirements are essential for maintaining a high level of interoperability and deriving sustained value from their digital health investments.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
To ensure a successful integration, healthcare providers should adhere to several best practices:
- Comprehensive Needs Assessment: Clearly define clinical and operational needs to select a platform that aligns with existing workflows.
- Pilot Programs: Conduct small-scale pilot integrations to identify and resolve issues before a full rollout.
- Staff Training: Provide thorough training for all clinical and administrative staff on the integrated system.
- Data Governance: Establish clear policies for data ownership, access, and security to maintain compliance and trust.
- Vendor Collaboration: Work closely with both telehealth and EHR vendors to ensure seamless communication and issue resolution.
By following these strategic guidelines, healthcare organizations can unlock the full potential of their telehealth and EHR systems, creating a unified and efficient digital health environment. This synergy is critical for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care in the evolving healthcare landscape of 2026 and beyond.
| Key Integration Aspect | 2026 Standard & Benefit |
|---|---|
| Bidirectional Data Flow | Real-time sync of patient data, ensuring consistency and reducing errors across platforms. |
| FHIR & HL7 APIs | Industry-standard protocols enabling secure, granular, and efficient data exchange. |
| Integrated Clinical Workflows | Telehealth embedded in EHR for seamless scheduling, documentation, and medication management. |
| AI-Powered Automation | AI and ML automate data mapping and provide predictive insights for enhanced efficiency. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Telehealth-EHR Integration
The primary benefit is seamless data flow, ensuring patient information is consistent and accessible across virtual and in-person care. This reduces administrative burden, minimizes errors, and enhances the overall quality and continuity of patient care, significantly improving clinical workflows.
95% compatibility indicates that nearly all critical patient data points and workflows are automated between telehealth and EHR systems. This high level of integration ensures efficiency, reduces manual data entry, and provides clinicians with comprehensive, real-time patient records for informed decision-making.
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7 are industry standards for exchanging healthcare information electronically. They provide secure frameworks and standardized formats for data transfer, crucial for enabling robust and reliable integration between diverse telehealth and EHR platforms.
AI and machine learning significantly enhance integration by automating complex data mapping, predicting potential discrepancies, and providing intelligent insights. These technologies streamline workflows, improve data accuracy, and enable proactive clinical decision support within integrated systems, optimizing efficiency.
Common challenges include the complexity of legacy EHR systems, variations in data standardization, ensuring robust security and HIPAA compliance, and the significant initial cost and resource investment required for implementation. Overcoming these requires strategic planning and collaboration.
Conclusion
In 2026, the discussion around telehealth platforms inevitably circles back to their integration capabilities with EHR systems. Achieving over 95% compatibility is no longer a luxury but a fundamental requirement for healthcare providers aiming to deliver efficient, safe, and patient-centered care. The journey towards this seamless synergy involves leveraging advanced APIs, adhering to interoperability standards, and strategically implementing solutions that embed telehealth directly into the clinical workflow. As technology continues to evolve, further driven by AI and machine learning, the future promises even deeper, more intelligent integrations, transforming healthcare delivery and ensuring that patient data empowers, rather than hinders, clinical excellence.